10 Essential Economic Indicators for Forex Trading
It is a well-known fact that many successful experienced traders use both technical and fundamental analysis during their trading process. The latter one looks at several economic indicators of different nations in order to determine, how they affect the currency exchange rates.
However, focusing only on one particular indicator might not be enough to come up with accurate Forex predictions. This is why in this article we will discuss 10 major economic indicators, which have a significant influence on the exchange rates and at the same time are relatively simple to understand. The full list of those items is as follows:
- Central bank interest rates
- Real Gross Domestic Product growth rate
- Unemployment Rate
- Inflation
- Trade balance
- Budget balance
- Stock market indices
- Commodity prices
- Bond yields
- Retail sales
In order to conduct thorough fundamental analysis, it is always a better idea to check all of those indicators, before coming up with conclusions. Analyzing a given currency pair with just one economic measure can be very misleading and potentially can lead to some serious losses. On the other hand, an analysis that involves several indicators can certainly help traders and investors to get a full picture of the economic performance of countries and their influence on the exchange rate dynamics. So let us now discuss each of those measures in more details:
Central Bank Key Interest Rates
Perhaps one of the most influential factors for determining the direction of the exchange rates is the key interest rates. Those are usually set by central banks, members of which meet regularly to discuss the future path of the monetary policy.
The actual key interest rate also determines the rates on loans and savings accounts in a given country. For example, if the European Central Bank charges commercial banks 3% for borrowing money, there is no point for them to led their customers at 1%, since bankers will only make some losses. So the process of how those financial institutions determine what rate to charge to customers is as follows: they take the current key interest rate, add some margin, in order to cover salaries, rent costs, taxes, and other expenses, and finally add the appropriate risk premium. The latter part means that clients who have a very solid credit rating will pay lower rates, than ones with lower credit scores.
So as we can see the central bank interest rates are one of the key factors in setting the interest rates on all loans, whether it will be a mortgage, consumer loan, credit card, or a car loan. So if some at some stage, policymakers, decide to cut rates, it can certainly help to stimulate the economy, since customers will now be able to borrow funds at much more affordable rates and spend less money on the interest expense.
The central bank interest rates also have a decisive influence on how much return do depositors earn on their savings accounts and certificates of deposit. In fact, they also determine how much interest swap traders can earn or pay on given currency pairs. So if the policymakers decide to hike rates this can certainly increase demand for a currency and lead to its appreciation. The obvious reason for this is the fact that savers will receive higher returns on their savings accounts and CDs, while Forex traders can earn higher swaps for holding a long position for a given currency.
As a result, everything else being equal, higher-yielding currencies tend to appreciate against the lower-yielding ones. To illustrate this we can take a look at this daily AUD/USD chart:
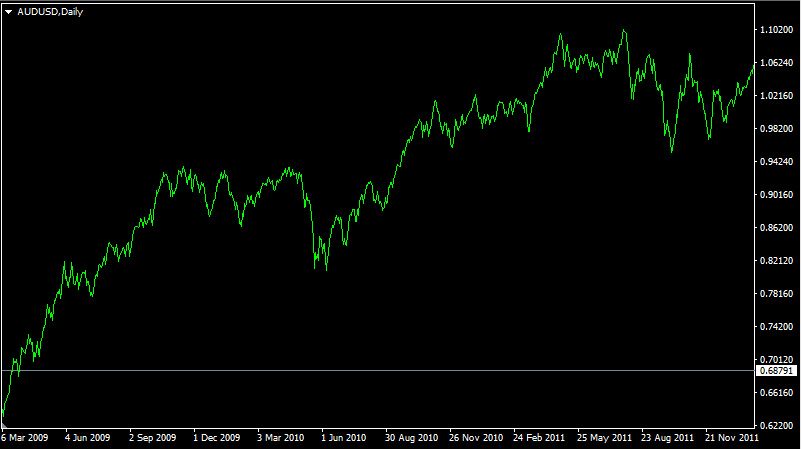
From December 2009 until December 2015, the US Federal Reserve has kept its Federal Funds rate unchanged holding it withing 0% to 0.25% range. On the other hand, the Reserve Bank of Australia has raised rates from 3% in 2009 to 4.75% before the end of 2010. So for many years, the Australian dollar was much higher-yielding currency, then USD. As a result, many traders used a long AUD/USD position for carry trading, earning some regular payouts in the process.
As we can see from the chart above, the Australian dollar has made steady gains from 2009, until early 2011. there were some major pullbacks, however, the overall direction of the trend seems very clear. During this period, the AUD/USD exchange rate has risen from 0.62 to 1.06. This means that in two years the Australian dollar has risen by approximately 71%, which is quite a rare development among the major currency pairs. By the end of 2010, the Reserve Bank of Australia ended its series of rate hikes, as a result, the AUD/USD exchange stabilized and started to move mostly sideways.
Real GDP Growth Rate
Obviously, the interest rates are not the only factors affecting the currency exchange rates. The Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rate is an essential indicator for measuring the economic performance of a nation. The nominal GDP calculated the total value of goods and services, produced within a country for a specific quarter or a year. One of the criticisms of this measure is the fact that it makes calculations on the raw amount of dollars, withing taking into account the changing purchasing power of the currency. The fact is that $1 today most likely will not the same buying power during the next year, so ignoring this fact can lead to misleading conclusions.
So the real GDP addresses those concerns by taking into account the inflation rate. For example, let us suppose that a nominal GDP of a nation is $5,000 billion in 2019 and during the next year reaches $5,300 billion, with the inflation rate of 3%. This means that the growth rate of nominal GDP was 6%. However, it is clear that buying power of $5,300 billion in 2020 is not 6% higher than $5,000 billion in 2019, due to a rise in the general price levels. So in order to calculate the Real GDP growth rate, we need to subtract the inflation rate from the nominal GDP growth rate. This is also called the use of deflator. So in this case, the Real GDP growth rate will be 3%.
The high GDP growth rate is a sign of a strong economy and does have the potential to increase the returns on the stock market and real estate investments. Also in this environment, the central bank is more likely to raise the interest rates and make the deposits and carry trades with that currency more lucrative. So this is why having a high Real GDP growth rate can be beneficial for the exchange rate of a given currency.
Unemployment Rate
Another major measure of economic performance is the unemployment rate. This indicator measures the percentage of unemployed people from the overall labor force. Having a high jobless rate is a sign of a weak economy and creates several problems.
Firstly, it indicates the scale of wasted potentials, since there can be hundreds of thousands of people, being able to work, pay taxes and contribute to the economy, but they do not have jobs. Secondly, countries whose high jobless rate also struggle with property problems. This makes sense since without having regular wages at hand, many people struggle to meet their basic daily needs, like shelter, food, and clothing. Finally, this is always problematic for the government finances, since it has to pay a large amount of unemployment benefits, with less revenue coming from payroll and income taxes.
This is because of those considerations that reducing unemployment is usually beneficial for the currency in question and supports its exchange rates.
Inflation
Inflation is yet another major factor that plays a crucial role in determining exchange rates. This measures the growth rate of overall price levels. The most famous indicator of measuring inflation is the Consumer Price Index (CPI). The basic principle for calculating this measure is that the relevant statistical agency employees will collect the latest prices of thousands of goods and services in the country and compare the results with previous year’s levels, while at the same time, applied weights to each category.
For example, in the case of the US CPI, housing makes up more than 42% index, when the transportation and foods and beverages categories each have close to 15% weight in the CPI. Due to different consumption patterns, the exact methodology of calculating the Consumer Price Index varies from country to country.
We have already discussed that the central bank interest rates are important for the exchange rates. However, here we need to keep in mind that those are nominal interest rates. However, as a famous financial expert, Axel Merk pointed out during one of his interviews, then those are the real interest rates that have a very profound impact on the exchange rates. The reason behind this is that most traders and investors are more interested in real returns, rather than nominal ones.
For example, by June 2020, the Turkish central bank has a key interest rate at 8.25%. Considering that ECB is holding rates at 0% and most other central banks keep rates within -0.1% to 0.25%, logically the Turkish lira has to be one of the strongest performing currencies in 2020. So why this is not the case? Well, the answer lies exactly in the inflation rate, which has reached 10.9%.
This means that the Turkish lira is losing its purchasing power rapidly. Having an 8.25% return is not much help if inflation is at 10.9%. This means that the real interest rates in Turkey currently stand at -2.65%. So this is one of the reasons, why the Turkish lira is still losing ground against major currencies.
So conducting this type of analysis can also be useful for predicting the exchange movements. Here, we can take a look at the real interest rates of the major currencies in June 2020:
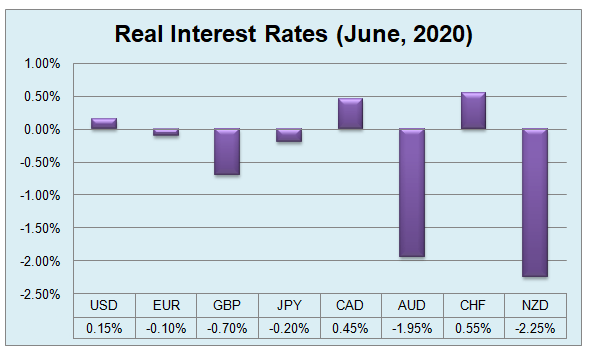
This seems very illogical that in June 2020, the Swiss Franc has the highest real interest rates. The country is currently experiencing a -1.3% annual deflation. The Swiss National Bank has cut rates to -0.75% some years ago to weakened Franc and stimulate inflation, but it brought no tangible results. It seems that the negative interest rate policy is not so effective.
The reason for this is very simple, people parking their savings in Swiss francs do not have to pay 0.75% for the privilege. They can move those funds to the CHF current account, or put the physical Swiss francs in the safe to avoid those charges. In this case, for them, the real interest rate will be at 1.3%, since during deflation the physical cash gains some buying power over time.
Due to current inflation levels, the US dollar and the Canadian dollar both have positive interest rates. The Euro, British pound, and Japanese yen are still into negative territory. Due to relatively higher inflation rates, the Australian dollar and the New Zealand dollar have quite notable negative interest rates. Here it has to be mentioned that at some point this picture can change substantially. If CPI rates in those countries keep rising, then at some stage, Australia’s and New Zealand’s central banks might consider interest rate hikes to preserve the price stability in their respective economies.
Trade Balance
Next on our list of important economic indicators for the Forex market is the trade balance. This measures the difference between the total value of exports and imports in a given country. So what does this have to do with exchange rates? Well, there are several arguments in favor of linking those two indicators.
If the total value of a country’s exports exceeds imports, then it is said that the nation has a trade surplus. This is beneficial in two ways. Firstly, in order to purchase goods and services, foreign individuals and businesses have to exchange their currency to the local currency. This just how the process works. So this creates a natural demand for the currency in question.
The trade surplus also has another benefit for the economy. One of the four components of the gross domestic product is the category called ‘Net Exports’. So if the value of the country’s total exports are higher than imports, than the difference is added to GDP. So essentially this promotes a higher rate of economic growth, helping the appreciation of the currency in the process.
Budget Balance
The budget balance is another important item on the list of most essential economic indicators for the Foreign exchange market. The formula here is very simple. It is calculated by subtracting the government expenses from its revenues. If the income is higher than outlays, then it is called the budget surplus. In the case of the opposite scenario, it is said that the government is running a budget deficit.
The fiscal policy can have significant implications on the exchange rates. If the government reduces the budget deficit or even achieves a budget surplus, this improves the investor confidence in the nation’s finances and it’s currency. This was one of the driving forces of the persistent appreciation of the US dollar against the other major currencies from 1995 to 2001. During those years the US government finances steadily improved, with the high water mark being the year 2000, when the country achieved a budget surplus of $236 billion.
On the other hand, if the public spending gets out of control, sooner or later, at some point the bond investors will lose confidence in the government’s ability to meet its debt obligations. As a result, they will demand higher interest rates, leading to the sovereign debt crisis. This already happened with several Eurozone countries several years ago, eventually bringing the entire future of the Euro project into question. This was also followed by the depreciation of EUR against some of its peers. To bring one example, during the summer of 2008 the Euro reached $1.59 level against the dollar, however, by 2015, it already fell below $1.15 level.
So here we can conclude that the sovereign debt crisis can potentially have very damaging effects not only on the country’s economy but to its currency as well.
Stock Market Indices
The performance of the Stock market indices of a given country might not have a direct impact on the currency exchange rates, however, the latest developments on those markets can give out some clues about the overall health of the economy.
For example, the Gross Domestic Product numbers are typically polished 1 or 2 months, after the relevant period has passed. So this when more forward-looking indicators come into the play. One of those can be the latest developments in the Stock market. The dramatic collapse in equity prices sometimes can be an early warning sign of an upcoming economic downturn.
The effects of such important moves can also extend to the Forex as well. The reason for this is that if the market sees the economy weakening, then it will assume that the central bank will respond by cutting rates and using other easing measures. Therefore, when a country faces a stock market collapse, it can be followed up by depreciation of its currency.
Commodity Prices
When reading the Forex trading news, we often hear the term ‘Commodity Currencies’. This term usually extends to the currencies of those countries, which is the major producer of one of the commodities. For example, the exchange rates of the Canadian dollar is usually closely tied to oil prices. The reason for this is the fact, that as one of the largest producers of this commodity, Canadian government and businesses can certainly benefit from rising fuel prices, which can lead to higher tax revenues for the country and larger profits for companies.
The Australian dollar is mostly tied to the gold price, for Australia is one of the largest producers of precious metals. In the case of New Zealand, dairy products make up a significant portion of its export, therefore NZD is usually highly correlated with those commodities.
Turning to some real-life example, for the purpose of better visualization, we can take a look at this daily EUR/CAD chart:
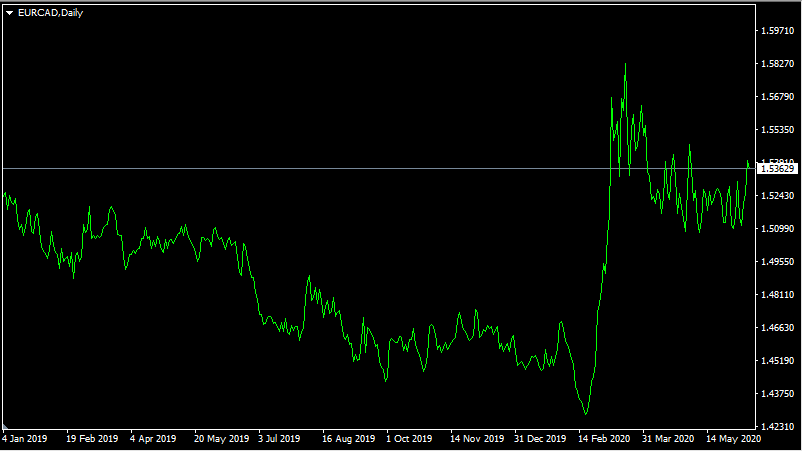
As we can see from the chart above, during 2019 the Canadian dollar made steady against the Euro, with EUR/CAD falling from 1.51 to 1.44. This coincided with the rise in oil prices. During the course of the year, the price of this commodity has risen from $48 to $61.
The direction of the trend change from February 2020, the oil prices started to collapse falling from $61 to briefly even going negative. The result was predictable, as EUR/CAD made some rapid gains, rising from 1.42 to 1.58. After April 2020, the oil prices recovered, eventually returning to $35 during the following months. This had the effect of moderating EUR/CAD exchange rates, reducing it close to 1.54 level. So as we can see from this example, in many cases, the developments in commodity prices can have a significant impact on the exchange rates of some currencies.
Bond Yields
Not all investors confine their investments to CDs, stocks, and real estate. Some of them also invest in government bonds. When it comes to the developed countries with a good credit rating, it is generally considered as a safe investment. The process is very straightforward: investors purchase bonds for maturities ranging from 1 week to 30 years and they get some interest in return. The short term treasuries are usually sold at a discount so that investors can earn some returns upon their maturities. In the case of longer-term bonds, the governments usually pay interest, called ‘coupon’ every 6 months.
Consequently, when the bond yields rise, the currency becomes more attractive to the investors, since now they are able to earn a higher return on government-issued securities. In order to purchase those assets, the market participants firstly have to buy the local currency. Therefore, everything else being equal, high bond yields tend to support the exchange rates of the currency.
Retail Sales
Finally, the last item on our list of the most important economic indicators is retail sales. In the case of nearly all of the countries, household consumption is the largest component of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). In the case of the US, this makes up 2/3 of the country’s GDP. Therefore the latest developments in consumer spending can have a major impact on economic growth.
One of the measures of this is the retail sales indicator. This is usually published on a monthly basis. Some small percentage changes in this indicator are very typical and usually do not have much influence on the exchange rates. However, if this indicator falls significantly, it can provide investors and traders with an early warning sign of the possible upcoming recession.
The reason behind this is the fact, that if people reduce their expenditures, the consumption component of the GDP will also fall significantly. This in turn can notably slow the rate of the economic growth of a given country and if the reduction is severe enough it can also lead to a contraction of the economy. Also, reduced consumer spending can also lead to a decline in business capital expenditures as well, to somehow offset the losses of the revenue. So the negative effects on GDP here can be even larger than originally expected. Most traders and investors are aware of this fact, therefore the falling retail sales of a given country are usually accompanied by the selloff of its currency.
On the other hand, rising retail sales can certainly lead to increasing the size of the consumption component in GDP, leading to a higher rate of economic growth. This can also can have a positive effect on business investment as well. Facing increasing consumer confidence, companies will be more likely to increase their capital expenditure in order to expand their commercial activities.
Important Economic Indicators in Forex Trading – Key Takeaways
- When it comes to the fundamental analysis in Forex, there is no one best failproof indicator. Professional traders and investors usually take several measures into the account, in order to come up with the full picture of factors, influencing the exchange rates. Therefore, analyzing only one indicator can be very misleading and potentially lead to wrong conclusions and loss of a significant amount of capital in Forex. For example, one currency might have high-interest rates, however, it might not appreciate against its peers due to a high level of inflation, unemployment, and other negative factors.
- Real interest rates can be a major factor in determining the exchange rate movements. Indeed, there are many emerging market currencies, which have high yields, however, in the long term, they still tend to depreciate against low-yielding major currencies. One of the possible reasons for this is that those developing countries have high levels of inflation, therefore when factoring in the Consumer Price Index, the real returns for investing in some of those currencies may not be as impressive as it would seem from just observing at their nominal interest rates.
- Some currencies like the Canadian dollar, Australian dollar, and New Zealand dollar, are called ‘Commodity Currencies’. This is because the exchange rate of CAD is usually highly correlated with the oil price, AUD mostly moves with gold, and NZD is generally tied to diary prices. Some investors and traders use those currencies as proxies to invest in those commodities, avoid storage charges, potentially earn some interest, and even benefit from the price rise of those assets in the process.
























Comments (0 comment(s))