Top 3 Fast-Food Stocks for Income and Growth Investors
In times of uncertainty and economic downturn, stocks that can deliver long term growth and increasing dividends are in high demand. However, the shares of Consumer Goods companies and Beverage Producers are not the only top performers in a recession. Fast food stocks also experienced steady growth. This trend became even stronger during the last couple of decades.
When it comes to this industry, it goes without saying that McDonald’s (MCD) is one leading player in the sector. It is the largest restaurant chain in the world by revenue. The company is the second-largest private employer in the world, having more than 1.7 million employees. The firm runs more than 37,000 outlets across the globe and operates in 119 countries. The restaurant has more than 145 items on the menu, including the famous Big Mac, Big N’ Tasty, McChicken, Filet-O-Fish, and others. According to the Chicago Tribune, McDonald’s serves more than 69 million customers on a daily basis.
The second stock on our list is Restaurant Brands International Inc (QSR). The company was formed back in 2014. In August 2014, the US Fast-food chain Burger King acquired the Canadian restaurant chain Hartons for C$12.5 billion. At the same time, the company also moved its headquarter in Toronto, Ontario. The main reason behind this was to reduce tax liabilities. Nowadays the firm operates more than 25,000 locations across the globe.
Yum! Brands Inc (YUM) is another famous fast-food company. The firm owns such famous brands as KFC, Pizza Hut, Wingstreet, and Taco Bell. Actually, before 1997 those brands were part of PepsiCo’s fast food division. The company operates more than 46,000 restaurants across the world.
Best Fast-Food Stocks for Investing
When it comes to restaurant stocks, we clearly have to make a distinction. Companies that operate upscale expensive dining locations might not really have the same degree of stable revenue growth as fast-food firms. The obvious reason behind this is that in times of economic downturn, many consumers might cut back on their visits to pricy restaurants.
Therefore, in this article we will focus on fast-food stocks:
- McDonald’s Corp (MCD)
- Restaurant Brands International Inc (QSR)
- Yum! Brands Inc (YUM)
Before we move on to discuss those individual stocks, there is one question. How do those firms manage to increase their revenues and dividends consistently over the years? Well, there are several reasons for this:
- It is easier for fast-food firms to build customer loyalty. After several visits, consumers remember their favorite menu items. So it is more likely that they will buy those foods on a regular basis.
- The prices of fast-food menu items are quite affordable. In times of crisis, customers might give up visiting expensive dining restaurants. However, it is unlikely that they will let go of their favorite $5 burger or $2 French fries, just to save some money.
- Nowadays customers do not have to visit those restaurants to taste their food. They can just order their favorite menu items and get it delivered at their doorstep.
Those arguments do not imply that all fast-food companies are successful. Some restaurants might fail due to poor management. So we will discuss those firms which have a solid track record.
McDonald’s Corp (MCD)
McDonald’s Corporation had a consolidated revenue of $21.1 billion in 2019. During this year global sales increased by 5.9%. Its current market capitalization is just above $134 billion. The net income for the year reached $6 billion, 14% higher than back in 2018. Earnings per share also expanded by 5%. During the year the company’s capital expenditure reached $2.4 billion. The firm mostly spent those funds to reinvest in its existing restaurants and fund. During the same period, the company managed to open 1,200 new restaurants.

McDonald’s also returned $8.6 billion to shareholders through dividend payments and share buybacks.
McDonald’s shares entered long term uptrend from 1995. Adjusting for stock splits, by that time one share was worth around $15. MCD has a strong showing for the next 4 years, reaching $48 by the end of 1999.
Despite this appreciation, the stock faced a sharp correction and by early 2003 it surrendered all of its gains. However, it was just a buying opportunity for many new investors. The stock rallied for the next 17 years. Even during the high of the great recession, MCD only lost 12%, only to regain all of its losses in just 3 months. By February 2020, the stock was trading at $217.
The outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdowns led to the stock market crash in March 2020. As a result, McDonald’s shares fell to $137. However, at the end of the same month, the firm published its quarterly results, which showed that revenue losses were not as dramatic as some people expected. As a result, the stock recovered and nowadays in May 2020, it is trading near $173.
McDonald’s Dividends and Other Indicators
McDonald’s has quite an impressive track record of dividend increases. Adjusting for stock splits, back in 1995 the company paid 13 cents a share.
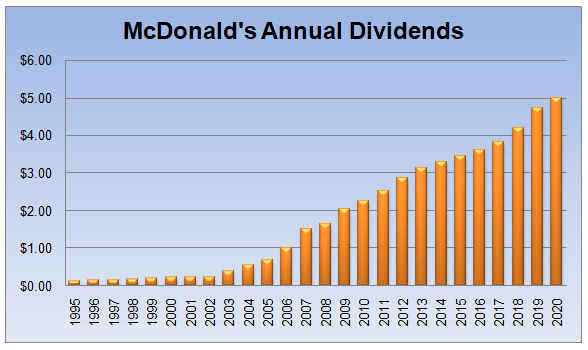
As we can see from this chart the firm steadily increased its payouts to shareholders. For example in 2007 the company hiked its annual dividend from $1.00 per share to $1.50 per share. 50% increase in a year is very rare indeed, even among the most successful businesses. In 2009, during the great recession, the management still raised the payout to shareholders by 25.8%. At the same time, many firms reduced or eliminated dividends because of economic challenges.
By 2020, the quarterly McDonald’s dividend has reached $1.25 per share. This brings the total of 4 payments to $5.00. However, when we get to December, it might be even higher, since the company usually hikes its payments during this time.
Those numbers suggest that the current Mcdonald’s dividend is more than 38 times higher than 25 years ago. The average growth rate of those payments is 15.7%, much higher than even some of the best blue-chip stocks. The current dividend yield of this stock is near 2.9%.
According to the official annual reports, the company spent at least $25 billion to shareholders through dividends and share buybacks during the 3 year period, ending in 2019.
As for the other indicators, the current earnings per share (EPS) stands at $7.63. This suggests that the price to earnings (P/E) ratio is 22.7. So the stock might not be cheap, but it is not too much into overvalued territory. The stock has a beta of 0.50. So Dow Jones Industrial Average is twice more volatile than MCD. This might benefit those investors who want to hold on to as much of their net worth as possible during the recession.
Restaurant Brands International Inc (QSR)
In 2019 Restaurant Brands International reported $5.603 billion in annual revenue. This was 4.6% higher figure than in 2018. The firm also posted $1,109 billion net income. During this period the company opened 1,342 new restaurants. 1,000 from those outlets are operating under the Burger King brand, which had a sales growth of 9%. The net restaurant sales growth for the year has reached 5.2%.

As mentioned before QSR started trading on the stock market in 2014. Originally one share was worth $35.41. For the first year, the stock experienced very little fluctuation, gradually falling to $32 by the end of January 2016. However, QSR started appreciating from the next month. The rally lasted until late August 2019. By that time the stock was worth around $78.
This was the high watermark of the QSR. During the following months, the stock began to slide. However, the worst decline came in February-March 2020, when it collapsed to $32. The shares of the company recovered in subsequent months and by May of 2020, they trade near $51 mark.
At the beginning of 2015, the company paid a quarterly dividend of 9 cents per share. During subsequent years the firm has increased shareholder payouts consistently. The largest increase came in 2018, as the management has decided to hike dividends by massive 114%, taking it from 21 cents per share to 45 cents per share.
The latest change came in 2020 when the company increases the rate of payments to shareholders to 52 cents per share, 4% higher than a year ago. So in just 5 years, Restaurant Brands International managed to increase its dividend by more than 5.8 times, or on average 42% a year. Obviously, in the long term, this might be unsustainable, but it is still quite impressive.
Restaurant Brands International Stock Valuations
The market capitalization of Restaurant Brands International is $23.4 billion. According to the latest figures, the earnings per share of the company stands at $2.32. Consequently, the price to earnings ratio is near 22. This might suggest that on purely P/E basis the stock price is just slightly above the fair valuation levels.
On the other hand, the dividend yield is near 4.1%. This can be quite attractive to income investors. As the US Federal Reserve returned to near-zero interest rates in 2020, it became increasingly difficult to earn decent returns on savings accounts and certificates of deposit. Nowadays even some online banks pay just 0.5% on 3-month CDs. So here investors have an opportunity to earn 8 times larger return on their investment. Obviously, unlike in the bank accounts, the principle of investment is not secure, so there is some element of risk. However, there is also a potential for capital appreciation in the long term. So those two points might balance each other out to some extent.
One interesting fact about the QSR is that its beta is 1.37. This is much higher than in the case of McDonald’s shares. So this stock might be a suitable investment for those investors who are looking for higher volatility.
The payout ratio of the company is near 77%. This suggests that in the foreseeable future firm’s dividend payments more or less seem secure. However, Restaurant Brands International might be forced to slow down on the rate of increases of those payments, to make this sustainable.
The company reported that during the first quarter its systemwide sales remained flat. Under usual circumstances, this is hardly a great achievement. However, in times when some companies have lost massive portions of their sales, this seems quite a decent result.
Yum! Brands Inc (YUM)
As David Gibbs, the Chief Executive Officer of Yum! Brands mentioned 2019 was a historic year for the company. During this time the firm opened its 50,000th restaurant. Systemwide sales have also surpassed $50 billion, 9% higher than back in 2018. At the same time, company revenue has reached $5.597 billion.
The company has also posted a net income of $1.294 billion. During this year Yum! Brands have returned $1.3 billion to shareholders by dividend payments and share repurchases.

As mentioned before this company was created back in 1997, as PepsiCo sold its fast-food division. The price of this transaction remained confidential, but many commentators believed that the deal was worth around $500 million.
By that time, one share was worth $5.44. During the subsequent years, the stock was rising steadily, eventually reaching $26 in August 2008. As the 2008 financial crisis hit the markets, YUM fell back to $19. However, this setback was only temporary. The stock resumed its long term uptrend from 2009 and rallied for the next 10 years.
In September 2019, Yum! Brands shares reached an all-time high of $119. The price began to moderate for the next few months. However, the biggest decline came in March 2020, when the stock fell sharply to $57. As the market recovered from the panic selling, YUM regained some of its losses. By May 2020 the stock trades near $84.
The earnings per share of the company stand at $3.59. So the price to earnings ratio is 15.9. It seems like the recent sharp market corrections gave investors an opportunity to buy YUM stock at relatively undervalued prices. On a purely P/E basis, Yum! Brands shares seem to be cheaper than in the case of MCD and QSR.
Yum! Brands Dividends and Other Measures
Yum! Brands have a quite decent track record of increasing dividend payments. It was back in 2004 when the firm started making regular quarterly payments to shareholders. Adjusting for the stock splits, by that time the dividend was 3.6 cents per share. Since then the firm steadily increased its payouts. In 2009, despite the economic challenges of the great recession, Yum! Brands still managed to raise its dividend by 10.5%.
The latest increase came in February 2020. The company raised its quarterly dividend by 11.9% to 47 cents per share. Therefore, on average, the firm increases its payouts to shareholders by 17.4%. This is a significantly higher number than in the case of many top dividend-paying stocks.
Another interesting thing on this subject is that the current payout ratio of the company is just below 56%. This suggests that Yum! Brands might still have plenty of ground to make substantial dividend increases during the next few years.
The standard 5 year beta of the stock is 0.87. This points to the fact that YUM is more volatile than McDonald’s shares. However, on average it fluctuates less than most other Nasdaq stocks. So in terms of volatility, it is in like a mid-point between MCD and QSR.
By the end of April 2020, the company published its first-quarter results. According to the report, systemwide sales fell by 3% with core operating profit declining by 6%. Despite those setbacks, it is worthwhile to keep in mind that many US companies suffered much higher losses in terms of their revenue and profitability. Consequently, Yum! Brands might be in a good position to recover and restore its sales to pre-2020 levels.
Investing in Fast Food Stocks – Key Takeaways
- Shares of Fast-Food companies are another example of ‘defensive stocks’. Those businesses enjoy customer loyalty for their products. The prices on their menu items are quite affordable, compared to upscale expensive restaurants. Finally, the majority of those firms do have a delivery service so consumers do not have to visit their outlets in order to consume their foods. Because of all of those reasons, fast-food companies are well-positioned steadily to increase their revenues and withstand the challenges in times of economic downturn.
- Several Fast-Food firms have a very solid track record of increasing dividend payments. Some of them on average have hiked their payouts by more than 15%. However, this is no the only way those companies return money to shareholders. They spend significant amounts on share buybacks. This is beneficial to investors since the purchased shares are taken out of circulation. As a result, there are fewer shares on the market and consequently, each of them becomes more valuable. This process also increases the percentage of ownership for each shareholder.
- The payout ratio can be an important indicator in stock analysis, especially for building an income portfolio. It measures what percentage of profits does the company distributes to its shareholders. If this measure is near 50% or below, this indicates that the firm’s payments to shareholders are very secure. If the Payout ratio is between 50% to 80% this suggests that the company is likely to manage those payouts. However, if this measure gets to 80% or higher, then this indicates that dividends are becoming unsustainable and eventually the management might be forced to cut the amount of those payments.
FAQ: Top Fast Food Stocks
Who are the largest shareholders of McDonald’s Corp, Restaurant Brands International, and Yum! Brands?
The Vanguard Group, Inc. one of the biggest mutual fund providers in the world is also the largest shareholder of McDonald’s. As of May 2020, the firm owns more than 66 million shares, which represent 8.9% of the company. The firm’s management allocates a significant portion of those shares into its income funds.
Interestingly Vanguard Group is also the largest shareholder of Yum! Brands as well. The mutual fund provider owns more than 23 million shares, which is the equivalent of a 7.65% stake in the fast-food giant.
The largest shareholder of Restaurant Brands International is RBC Dominion Securities, Inc. It is part of the wealth management division of the Royal Bank of Canada. At the moment it owns more than 8.7 million shares. This represents a 2.92% stake in Restaurant Brands International.
Why high payout ratios can be problematic for the company’s shareholders?
In order to answer this question, let us take one practical example. Suppose that the company has $5 billion in annual revenue and $1 billion in profits. At the same time, the management distributes $900 million as dividends. So the payout ratio of this firm would be 90%. This is problematic in several ways.
Firstly, after making those payments to shareholders the company treasury will be left only with $100 million. This might be a too-small amount compared to the firm’s size. As a consequence, the company is in a poor position to respond to unpredictable challenges, such as large fines, unexpected expenses, rising costs of raw materials, and many other possible problems.
Secondly, the sales and profit figures typically do not tend to be flat over the years. So if because of an economic downturn or some other reason firm’s revenues plummet, it has a very small safety margin to maintain its payments to shareholders.
As a result of those problems in many cases, companies are forced to cut their dividend payments and disappoint the investors in the process.
Why does the Economist use the price Big Mac, McDonald’s product, for its currency valuations?
There can be several possible reasons why the British financial journal Economist decided to create the so-called ‘Big Mac Index’. Here is a list of some of those:
- Big Mac is a well-recognized McDonald’s product across the world. It is sold in more than 110 countries. Since this product is available in so many nations, it gives analysts the opportunity to compare their prices between different regions.
- The composition of the Big Mac price represents some sort of basket of goods and services. It includes the price of bread, beef, cheese, lettuce, onions, cucumber, sesame seeds, cost of labor, transportation, rent, and taxes. So the Big Mac index can also be used to give us some idea of inflationary dynamics in a given country.
- It is very easy to measure. In the case of the Consumer Price Index, government employees have to collect thousands of prices across a huge range of goods and services. After collecting all of this date, then they have to apply different weights to come up with the final figure. Big Mac index is much easier to measure, all they have to do is to send some Economist’s employees in a number of McDonald’s restaurants, collect the price of this one product and then come up with average. Nowadays many prices are available online, so sometimes they do not even have to visit every single location to come up with necessary data.
























Comments (0 comment(s))